Management
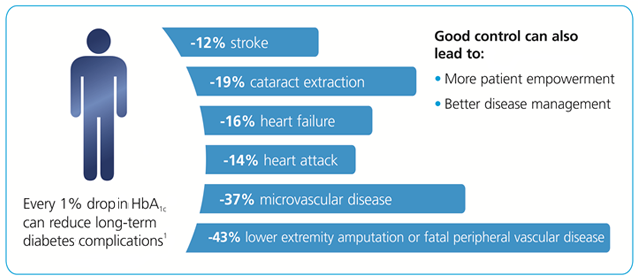
Each 1% reduction of HbA1c towards achieving glycemic control helps in reducing long term complications as shown below:
Good blood sugar control is an important ascpect of optimal diabetes management
Depending upon blood glucose levels, age, height and weight, and other associated complaints doctors prescribe medicines to a person with diabetes. Each type of treatment helps lower blood sugar in a unique way.
- For Type 1 diabetes- One needs to be treated with insulin injections every day. There are several types of insulin. Earlier, there was only conventional human insulin, now we have modern insulin’s or insulin analogues. In general modern insulin’s are more physiological, predictable and safe and also provide convenience and flexibility as they can be taken just before or even after eating.
- For Type 2 Diabetes- Type 2 diabetes is a progressive disorder. Treatment of diabetes is based on increasing availability of insulin in body. As, there is a continuous destruction of the insulin-producing beta cells over time, it leads to the addition of medications every few years. Adding insulin therapy also becomes essential after some time. It is very essential for the doctor to evaluate the patient at regular intervals to help the patient in a long run. Mostly all medications can act only till some of the insulin producing beta cells are still alive They can be classified in many groups-
ORAL
- Medication that Inhibit the production and release of glucose from the liver, which means one need less insulin to transport sugar into your cells E.g Biguanides
- Medications that stimulate the pancreas to produce and release more insulin. This class includes sulphonylureas and glinides.
- Medication that makes the body more sensitive to the insulin it produces. These types of drugs include the thiazolidinediones.
- Medication that decrease sugar absorption by the intestines. They are often prescribed in conjunction with other diabetes medications. E.g. Alpha-glycosidase inhibitors.
- Medications that enhance incretin hormone levels by inhibiting enzyme DPP-IV (Di peptidyl peptidase-IV), e.g. gliptins.
- SGLT2 inhibitors class of drugs that flushes more glucose out through urine.so that it does not get reabsorbed back into the body.
INJECTABLES
- Incretin based therapies that increase natural GLP-1 in body and stimulate pancreas to release insulin. GLP-1RA based therapies represent a new class of treatments for type 2 diabetes, where GLP-1 analogues similar to natural GLP-1 hormone is given from outside that lowers blood sugar levels by stimulating the release of insulin from beta cells.
- Insulin – Most of people with type 2 diabetes eventually require insulin. Modern insulin delivery devices have made taking insulin very easy.
Various Insulin Regimens
Many different types of insulin treatment are available and can successfully control blood sugar levels; It may take some time to find the right dose for any individual as insulin requirement is dependent on many factors. Insulin needs often change for these children (not so much in adults) especially during their growing years. Changes in weight, height, other hormones, diet, activity level, any stress (mental or physical) can affect the amount of insulin needed to control your blood sugar. It is important to check blood sugar level several times in a day to reach the right dose. There are two general types of insulin treatment plans:
- Standard (conventional) insulin treatment – In this regimen 2 doses of premixed insulin (short and long acting e.g. 30/70) before breakfast and dinner are given. Patients on this regimen need to have a fixed diet at the particular time, with least variations in activities to achieve the optimal glucose control. Although it is difficult to achieve best glucose control with standard insulin treatment, and people may require intensive insulin therapy
- Intensive insulin treatment - Intensive insulin treatment is best for keeping blood sugar in tight control especially for children with type 1 diabetes. In this regimen, child needs to take three or more insulin shots of short acting insulin along with main meals per day and one or two doses of long acting insulin for maintaining minimal requirement of insulin throughout the day. Doses of short acting insulin can be adjusted according to the food eaten.This regimen is most commonly used regimen for intensifying insulin treatment in adults as well.
- For convenience of patients, many different regimens which are mid-way between standard and intensive insulin treatment are suggested. These include;
- On dose of long acting insulin with one dose of short acting insulin with major meal
- Two doses of self-mixed dose of short acting and long acting.
- Two doses of short acting before breakfast and lunch and one dose of premixed insulin at night before dinner.
- Two doses of premixed insulin before breakfast and dinner and one dose of short acting before lunch.
Few key things which one need to keep in mind while on diabetes treatment-
- Any medication is only a part of the diabetes treatment plan and cannot be a substitute for a healthy diet and exercise.
- No single diabetes treatment is best for everyone, and what works for one person may not work for another. This is where your health care provider comes in. He or she can help determine how a specific medication or multiple medications may fit into your overall diabetes treatment plan.
- Each person need to understand from his/her doctor how often which medication needs to be taken. Before meal, in between meal or after meal.
Never self-medicate as only your doctor can judge about the diabetes management and the therapy suited best for you.
UKPDS: Stratton et al. BMJ 2000;32:405–12
David M. Nathan. Diabetes Advances in Diagnosis and Treatment. JAMA. 2015;314(10):1052-1062. doi:10.1001/jama.2015.9536







