
Healthy diet is not only essential for people with diabetes but for every one of us as it is the need of hour to prevent diabetes, hypertension, heart diseases and other life style disorders.
A diabetes meal plan is a guide that tells you how much and what kinds of food one should choose to eat at meals and snack times.
Some meal planning tools include:

Carbohydrate counting, or "carb counting," is a meal planning technique that helps you to keep track of how much carbohydrate you are eating.
Which foods have carbohydrates:
Starches
One starch exchange* contains approximate 15 grams of carbohydrate, 2-3gm protein , 0-1 gm. fat and 80 calories. Whole grains are always a better choice.
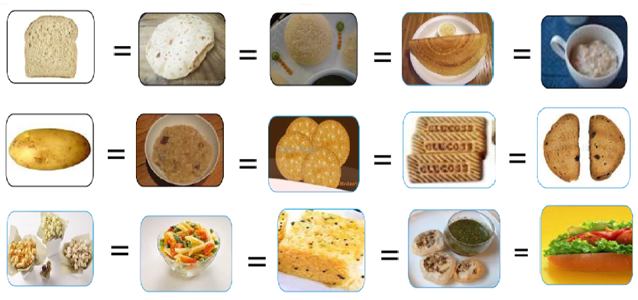
Bread 1 slice medium= 1 chapathi around 6 inches= Idli 3 inch round= 1 plain dosa= rice 1/3RD cup = 1small potato=oats ½ cup= 4 marie biscuit= 3glucose biscuits= 2 rusk = 3cup popcorns without fat =1/2cup pasta or noodles = dhokla 1 square = 3 pani poori = ½ hot dog
http://www.diabetesindia.com/diabetes/fruitsexchange_list.htm accessed on 22nd April 2015
Fruits
One exchange of fruit* contains approximate 15 grams of carbohydrate, no protein or fat, and 60 calories. Fruits should be taken along with edible skin and seeds.
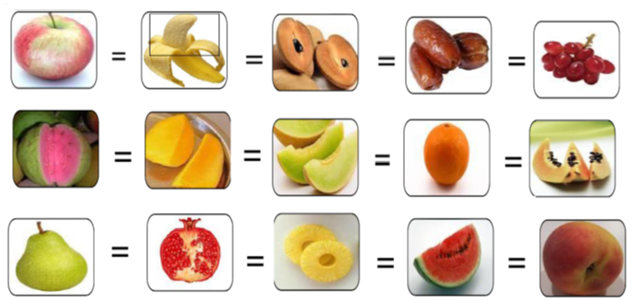
Apple, small (2 inches)½= Banana (9 inch long)=1 small cheekoo (saputa) = 15 grapes= 1 guava medium= ½ mango small or 1 slice large= ¼ medium musk melon or 3 slices = 3slices of papaya = 1orange = 1medium pear = ½ pomegranate= 2slices of pineapple= 1medium peach
http://www.diabetesindia.com/diabetes/fruitsexchange_list.htm accessed on 22nd April 2015
Carbohydrate content (CHO) of common food items
| Menu | Quantity | CHO Content(gms) |
|---|---|---|
| Cooked Rice | 1/3 Cup | 15 |
| Chapati 1 medium 6 Inch | 1 medium | 15 |
| Vegetable (Non Starchy) | 1 Cup | 5 |
| Poha | ½ Cup | 15 |
| Curds | ½ Cup | 6 |
| Milk | 1 Cup | 12 |
| Apple | 1 small | 15 |
Low GI Foods (55 or less)
Medium GI (56-69)
High GI (70 or more)
American Diabetes Association. Last edited July 1, 2015
