
One of the key programs NNEF has been implementing is the Changing Diabetes Barometer program. It had partnered with many progressive State Governments across India, viz., Goa, Bihar, Gujarat, Pondicherry, Andhra Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh & Odisha. Presently the program is ongoing in the state of Goa and Karnataka.
The Changing Diabetes Barometer (CDB) is a NNEF initiative that aims at responding to the global dia¬betes pandemic by collecting and sharing data for diabetes care worldwide. In addition to collecting exist¬ing data, CDB encourages the measurement of outcomes and facilitates sharing of knowledge so that doctors, people with diabetes, and other stakeholders can integrate the data and learn what works in which conditions. It is aimed at driving improvement of diabetes care thereby saving human lives and reducing the economic burden on healthcare systems and society.
The main objective of CDB is to place people with diabetes and the importance of quality of care at the centre of the CDB initiative. The best way to do this is through measuring and sharing data to increase awareness and the need for improvements in diabetes prevention, treatment, and care. Furthermore, it will provide a context in which healthcare providers and payers can analyse the performance of their own efforts, benefit from the example given by others and drive improvements in diabetes care.
CDB initiatives are aimed to achieve the following results:
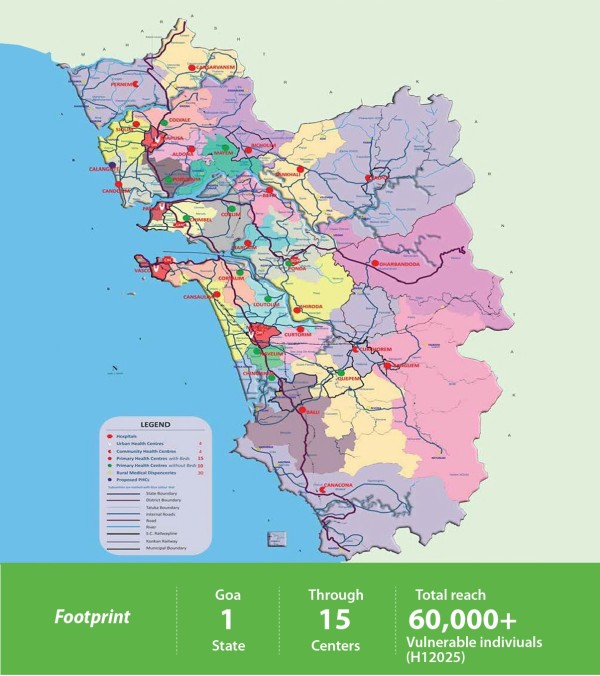
*The map above is for illustrative purposes and is not drawn to scale
One of the key programs NNEF has been implementing is the Changing Diabetes Barometer program. It had partnered with many progressive State Governments across India, viz., Goa, Bihar, Gujarat, Pondicherry, Andhra Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh & Odisha. Presently the program is ongoing in the state of Goa and Karnataka.
The Changing Diabetes Barometer (CDB) is a NNEF initiative that aims at responding to the global dia¬betes pandemic by collecting and sharing data for diabetes care worldwide. In addition to collecting exist¬ing data, CDB encourages the measurement of outcomes and facilitates sharing of knowledge so that doctors, people with diabetes, and other stakeholders can integrate the data and learn what works in which conditions. It is aimed at driving improvement of diabetes care thereby saving human lives and reducing the economic burden on healthcare systems and society.
The main objective of CDB is to place people with diabetes and the importance of quality of care at the centre of the CDB initiative. The best way to do this is through measuring and sharing data to increase awareness and the need for improvements in diabetes prevention, treatment, and care. Furthermore, it will provide a context in which healthcare providers and payers can analyse the performance of their own efforts, benefit from the example given by others and drive improvements in diabetes care.
CDB initiatives are aimed to achieve the following results:

*The map above is for illustrative purposes and is not drawn to scale