Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to serious complications
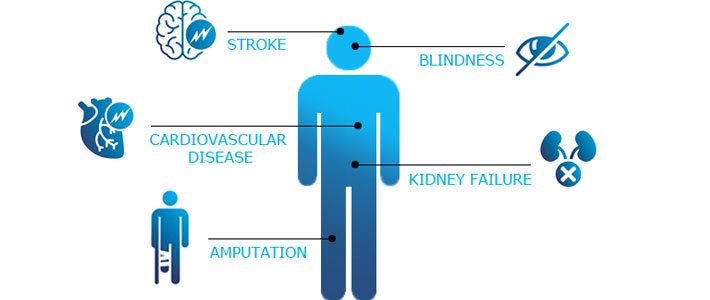

People with diabetes may have blurring and frequent fluctuations in vision, cataract at younger age, Glaucoma, decreased vision due to involvement of optic nerve, temporary paralysis of the muscles controlling the movement of eyes and thus double vision. The most significant complication that can cause blindness in people with diabetes is diabetic retinopathy.

Uncontrolled diabetes damages the small blood vessels in the kidneys, impairing kidney function and resulting in body retaining more water and salt than required. Wastes and fluid build up in blood. In addition when the kidneys are damaged, protein leaks out of the kidneys into the urine.

People with diabetes can develop nerve problems at any time, but the risk rises with age and longer duration of diabetes. The highest rates of neuropathies are seen in patients having diabetes for at least 25 years.

In people with diabetes, chances of having a stroke are 1.5 times higher than in people who don't have diabetes. A stroke happens when the blood supply to a part of brain is suddenly interrupted. The damage to blood vessels by high blood glucose levels makes it easier for fatty deposits to form in arteries and cause narrowing or blockages.

Heart disease strikes people with diabetes, twice as often as people without diabetes. More than 65 percent of deaths in diabetes patients are attributed to heart and vascular disease.
Uncontrolled diabetes can damage the feet in three ways- nerve damage, blood vessel damage and altered immune system due to high blood glucose levels. If left untreated, a minor foot injury could become a serious infection — even leading to tissue death (gangrene) requiring amputation.